Confidential Asset (CA)
Aptos 机密资产标准(也称为”机密资产”或”CA”)是一种用于管理同质资产(FA)的隐私协议. 它允许用户在隐藏 FA 金额的同时进行交易,同时保持发件人和收件人地址公开可见.
此标准允许任何 FA 包装成相应的机密资产,确保与现有代币的兼容性. 它支持 64 位传输,余额最高可达 128 位.
对机密资产余额(机密余额)的操作需要零知识证明(ZKP)来验证交易的正确性 而不透露隐藏金额和其他敏感数据.
机密资产存储
Section titled “机密资产存储”对于每个注册的机密资产,用户会生成一个唯一的密钥对:
- 存储在链上的加密密钥(EK).
- 用户安全保管的解密密钥(DK).
这些密钥是独立的,不应与用户的 Aptos 账户密钥混淆.
每个机密余额分为两部分:
pending_balance- 累积所有传入交易.actual_balance- 专用于传出交易.
两个余额都使用相同的用户 EK 加密,确保底层金额保持私密.
机密余额及其相关的加密密钥存储在 ConfidentialAssetStore 资源中.
ConfidentialAssetStore 为用户拥有的每个机密资产实例化,并由 confidential_asset 模块管理:
struct ConfidentialAssetStore has key { pending_balance: confidential_balance::CompressedConfidentialBalance, actual_balance: confidential_balance::CompressedConfidentialBalance, ek: twisted_elgamal::CompressedPubkey, // ...}机密余额通过将代币金额分割成称为块的小单位来处理. 每个块代表总金额的一部分,并使用用户的 EK 单独加密. 这种设计确保了余额的高效管理.
待处理余额由四个块组成,持有所有传入转账. 它可以在需要滚动到实际余额之前处理多达 2^16 个 64 位转账. 在此累积过程中,待处理余额块可以增长到每个 32 位.
实际余额由八个块组成,支持 128 位值. 在任何操作之后,实际余额应归一化回 16 位块以保持高效解密.
confidential_balance 模块中的 ConfidentialBalance 结构用于表示待处理和实际余额:
struct ConfidentialBalance has drop { chunks: vector<twisted_elgamal::Ciphertext>,}加密包括:
- 将总金额分割成 16 位块.
- 应用用户的 EK 单独加密每个块.
解密包括:
- 应用用户的 DK 解密每个块.
- 为每个块解决离散对数(DL)问题以恢复原始值.
- 组合恢复的值以重建总金额.
归一化确保块始终减少到可管理的大小(16 位). 如果没有归一化,块可能会增长过大,使解密过程(解决 DL)显著变慢甚至不切实际. 此机制在每次操作后自动应用于实际余额, 确保用户始终可以解密其余额,即使余额通过多次交易增长. 只有在滚动后,用户才需要手动归一化实际余额.
该协议利用同态加密,允许对机密余额进行算术运算而无需解密. 此功能对于在转账期间更新接收者的待处理余额和滚动时至关重要, 用户的待处理余额被添加到实际余额中.
下图显示了机密资产模块之间的关系:
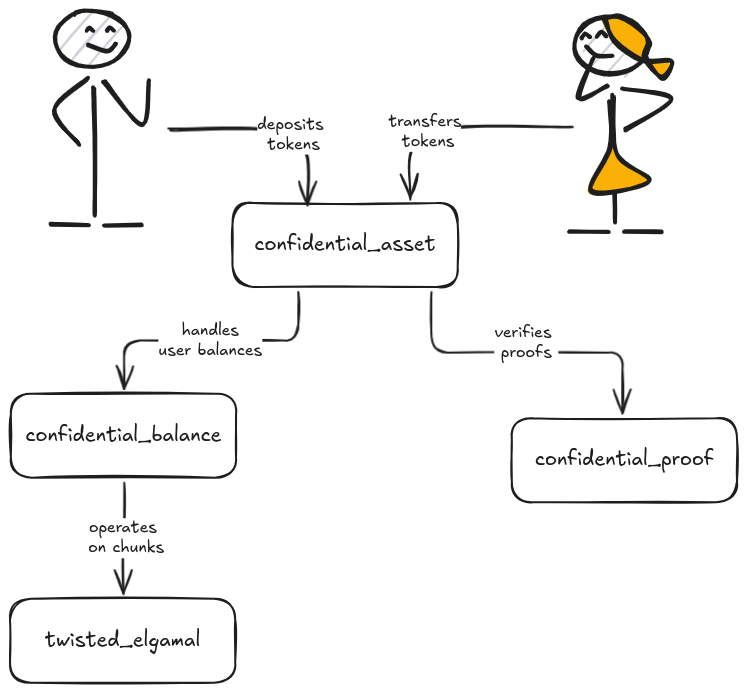
用户与 confidential_asset 模块交互以对其机密余额执行操作.
confidential_asset 模块调用 confidential_balance 模块来管理机密余额,并调用 confidential_proof 模块来验证 ZKP.
在底层,confidential_balance 模块使用 twisted_elgamal 模块对块进行操作.
public entry fun register(sender: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>, ek: vector<u8>)#[view]public fun has_confidential_asset_store(user: address, token: Object<Metadata>): bool用户必须为他们打算交易的每个代币注册一个 ConfidentialAssetStore.
在此过程中,用户需要在其端生成一个密钥对(EK 和 DK).
当 ConfidentialAssetStore 首次注册时,机密余额设置为零,
表示为 pending_balance 和 actual_balance 的零密文.
您还可以使用 has_confidential_asset_store 函数检查用户是否拥有特定代币的 ConfidentialAssetStore.
#[test_only]module confidential_asset_addr::register_example { /// ...
fun register(bob: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>) { let bob_addr = signer::address_of(bob);
// 这是一个仅用于测试的函数,因此我们不需要担心密钥对的安全性。 let (_bob_dk, bob_ek) = twisted_elgamal::generate_twisted_elgamal_keypair();
let bob_ek = twisted_elgamal::pubkey_to_bytes(&bob_ek);
confidential_asset::register(bob, token, bob_ek);
print(&utf8(b"Bob's pending balance is a zero ciphertext:")); print(&confidential_asset::pending_balance(bob_addr, token));
print(&utf8(b"Bob's actual balance is a zero ciphertext:")); print(&confidential_asset::actual_balance(bob_addr, token));
print(&utf8(b"Bob's encryption key is set:")); print(&confidential_asset::encryption_key(bob_addr, token)); }}public entry fun deposit(sender: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>, amount: u64)public entry fun deposit_to(sender: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>, to: address, amount: u64)deposit 和 deposit_to 函数将代币带入协议,从发送者的主要 FA 存储转移传递的金额
到接收者的待处理余额.
此函数中的金额是公开可见的,因为将新代币添加到协议中需要正常转账. 然而,协议中的代币通过机密转账变得模糊,确保后续交易的隐私.
#[test_only]module confidential_asset_addr::deposit_example { /// ...
fun deposit(bob: &signer, alice: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>) { let bob_addr = signer::address_of(bob); let alice_addr = signer::address_of(alice);
// 这是一个仅用于测试的函数,因此我们不需要担心密钥对的安全性。 let (bob_dk, bob_ek) = twisted_elgamal::generate_twisted_elgamal_keypair(); let (alice_dk, alice_ek) = twisted_elgamal::generate_twisted_elgamal_keypair();
let bob_ek = twisted_elgamal::pubkey_to_bytes(&bob_ek); let alice_ek = twisted_elgamal::pubkey_to_bytes(&alice_ek);
confidential_asset::register(bob, token, bob_ek); confidential_asset::register(alice, token, alice_ek);
print(&utf8(b"Bob's FA balance before the deposit is 500:")); print(&primary_fungible_store::balance(bob_addr, token));
assert!(primary_fungible_store::balance(bob_addr, token) == 500);
let bob_amount = 100; let alice_amount = 200;
// 余额尚未隐藏,因为我们明确将金额传递给函数。 confidential_asset::deposit(bob, token, bob_amount); confidential_asset::deposit_to(bob, token, alice_addr, alice_amount);
print(&utf8(b"Bob's FA balance after the deposit is 200:")); print(&primary_fungible_store::balance(bob_addr, token));
assert!(primary_fungible_store::balance(bob_addr, token) == 200);
print(&utf8(b"Bob's pending balance is not zero:")); print(&confidential_asset::pending_balance(bob_addr, token));
// 在现实世界中,我们无法看到其他人的余额,因为这需要 // 解密密钥的知识。 // 余额解密需要解决离散对数问题, // 因此我们只是简单地检查传递的金额是否正确。 assert!(confidential_asset::verify_pending_balance(bob_addr, token, &bob_dk, bob_amount));
print(&utf8(b"Alice's pending balance is not zero:")); print(&confidential_asset::pending_balance(alice_addr, token));
assert!(confidential_asset::verify_pending_balance(alice_addr, token, &alice_dk, alice_amount)); }}滚动待处理余额
Section titled “滚动待处理余额”public entry fun rollover_pending_balance(sender: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>)rollover_pending_balance 函数将待处理余额添加到实际余额中,将待处理余额重置为零.
它无需额外证明即可工作,因为此函数利用了协议中使用的同态加密的属性.
#[test_only]module confidential_asset_addr::rollover_example { /// ...
fun rollover(bob: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>) { let bob_addr = signer::address_of(bob);
// 这是一个仅用于测试的函数,因此我们不需要担心密钥对的安全性。 let (bob_dk, bob_ek) = twisted_elgamal::generate_twisted_elgamal_keypair();
let bob_ek = twisted_elgamal::pubkey_to_bytes(&bob_ek);
let bob_amount = 100;
confidential_asset::register(bob, token, bob_ek); confidential_asset::deposit(bob, token, bob_amount);
print(&utf8(b"Bob's pending balance is NOT zero:")); print(&confidential_asset::pending_balance(bob_addr, token));
print(&utf8(b"Bob's actual balance is zero:")); print(&confidential_asset::actual_balance(bob_addr, token));
assert!(confidential_asset::verify_pending_balance(bob_addr, token, &bob_dk, bob_amount)); assert!(confidential_asset::verify_actual_balance(bob_addr, token, &bob_dk, 0));
// 不需要显式归一化,因为实际余额已经归一化。 assert!(confidential_asset::is_normalized(bob_addr, token));
confidential_asset::rollover_pending_balance(bob, token);
print(&utf8(b"Bob's pending balance is zero:")); print(&confidential_asset::pending_balance(bob_addr, token));
print(&utf8(b"Bob's actual balance is NOT zero:")); print(&confidential_asset::actual_balance(bob_addr, token));
assert!(confidential_asset::verify_pending_balance(bob_addr, token, &bob_dk, 0)); assert!(confidential_asset::verify_actual_balance(bob_addr, token, &bob_dk, (bob_amount as u128))); }}public entry fun confidential_transfer( sender: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>, to: address, new_balance: vector<u8>, transfer_amount: vector<u8>, auditor_eks: vector<u8>, auditor_amounts: vector<u8>, zkrp_new_balance: vector<u8>, zkrp_transfer_amount: vector<u8>, sigma_proof: vector<u8>)confidential_transfer 函数将代币从发送者的实际余额转移到接收者的
待处理余额.发送者使用接收者的加密密钥加密转移的金额,使接收者的
机密余额能够同态更新.
为了确保透明性,发送者还可以使用审计员的 EK 加密转移的金额, 允许审计员在其端解密转移的金额.
#[test_only]module confidential_asset_addr::transfer_example { /// ...
fun transfer(bob: &signer, alice: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>) { let bob_addr = signer::address_of(bob); let alice_addr = signer::address_of(alice);
// 这是一个仅用于测试的函数,因此我们不需要担心密钥对的安全性。 let (bob_dk, bob_ek) = twisted_elgamal::generate_twisted_elgamal_keypair(); let (alice_dk, alice_ek) = twisted_elgamal::generate_twisted_elgamal_keypair();
// 注意:如果设置了资产特定的审计员,我们需要将其包含在 `auditor_eks` 向量中作为第一个元素。 // // let asset_auditor_ek = confidential_asset::get_auditor(token); // let auditor_eks = vector[]; // if (asset_auditor_ek.is_some()) { // auditor_eks.push_back(asset_auditor_ek.extract()); // };
let (_, auditor_ek) = twisted_elgamal::generate_twisted_elgamal_keypair(); let auditor_eks = vector[auditor_ek];
let bob_ek_bytes = twisted_elgamal::pubkey_to_bytes(&bob_ek); let alice_ek_bytes = twisted_elgamal::pubkey_to_bytes(&alice_ek);
confidential_asset::register(bob, token, bob_ek_bytes); confidential_asset::register(alice, token, alice_ek_bytes);
// Bob 的当前余额为 300,他想转账 50 给 Alice,Alice 的余额为零。 let bob_current_amount = 300; let bob_new_amount = 250; let transfer_amount = 50; let alice_current_amount = 0; let alice_new_amount = 50;
confidential_asset::deposit(bob, token, bob_current_amount); confidential_asset::rollover_pending_balance(bob, token);
print(&utf8(b"Bob's actual balance is 300")); assert!(confidential_asset::verify_actual_balance(bob_addr, token, &bob_dk, (bob_current_amount as u128)));
print(&utf8(b"Alice's pending balance is zero")); assert!(confidential_asset::verify_pending_balance(alice_addr, token, &alice_dk, alice_current_amount));
let current_balance = confidential_balance::decompress_balance(&confidential_asset::actual_balance(bob_addr, token));
let ( proof, // 新余额是转账后使用发送者的加密密钥加密的余额。 // 它将被设置为发送者的新实际余额。 new_balance, // 使用接收者的加密密钥加密的转账金额。 // 它将同态地添加到接收者的待处理余额中。 transfer_amount, // 使用审计员的加密密钥加密的转账金额。 // 它不会存储在链上,但审计员可以使用其 dk 解密转账金额。 auditor_amounts ) = confidential_proof::prove_transfer( &bob_dk, &bob_ek, &alice_ek, transfer_amount, bob_new_amount, ¤t_balance, &auditor_eks, );
let ( sigma_proof, zkrp_new_balance, zkrp_transfer_amount ) = confidential_proof::serialize_transfer_proof(&proof);
confidential_asset::confidential_transfer( bob, token, alice_addr, confidential_balance::balance_to_bytes(&new_balance), confidential_balance::balance_to_bytes(&transfer_amount), confidential_asset::serialize_auditor_eks(&auditor_eks), confidential_asset::serialize_auditor_amounts(&auditor_amounts), zkrp_new_balance, zkrp_transfer_amount, sigma_proof );
print(&utf8(b"Bob's actual balance is 250")); assert!(confidential_asset::verify_actual_balance(bob_addr, token, &bob_dk, bob_new_amount));
print(&utf8(b"Alice's pending balance is 50")); assert!(confidential_asset::verify_pending_balance(alice_addr, token, &alice_dk, alice_new_amount)); }}public entry fun withdraw( sender: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>, amount: u64, new_balance: vector<u8>, zkrp_new_balance: vector<u8>, sigma_proof: vector<u8>)public entry fun withdraw_to( sender: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>, to: address, amount: u64, new_balance: vector<u8>, zkrp_new_balance: vector<u8>, sigma_proof: vector<u8>)withdraw 和 withdraw_to 允许用户从协议中提取代币,
将传递的金额从发送者的实际余额转移到接收者的主要 FA 存储.
此函数使用户能够释放代币,同时不透露其剩余余额.
#[test_only]module confidential_asset_addr::withdraw_example { /// ...
fun withdraw(bob: &signer, alice: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>) { let bob_addr = signer::address_of(bob); let alice_addr = signer::address_of(alice);
// 这是一个仅用于测试的函数,因此我们不需要担心密钥对的安全性。 let (bob_dk, bob_ek) = twisted_elgamal::generate_twisted_elgamal_keypair(); let (_alice_dk, alice_ek) = twisted_elgamal::generate_twisted_elgamal_keypair();
let bob_ek_bytes = twisted_elgamal::pubkey_to_bytes(&bob_ek); let alice_ek_bytes = twisted_elgamal::pubkey_to_bytes(&alice_ek);
confidential_asset::register(bob, token, bob_ek_bytes); confidential_asset::register(alice, token, alice_ek_bytes);
let bob_current_amount = 500; let bob_new_amount = 450; let transfer_amount = 50;
// Bob 提取所有可用代币 confidential_asset::deposit(bob, token, (bob_current_amount as u64)); confidential_asset::rollover_pending_balance(bob, token);
print(&utf8(b"Alice's FA balance before the withdrawal is zero:")); print(&primary_fungible_store::balance(alice_addr, token));
assert!(primary_fungible_store::balance(alice_addr, token) == 0);
print(&utf8(b"Bob's actual balance before the withdrawal is 500")); assert!(confidential_asset::verify_actual_balance(bob_addr, token, &bob_dk, bob_current_amount));
let current_balance = confidential_balance::decompress_balance(&confidential_asset::actual_balance(bob_addr, token));
let (proof, new_balance) = confidential_proof::prove_withdrawal( &bob_dk, &bob_ek, transfer_amount, bob_new_amount, ¤t_balance );
let new_balance = confidential_balance::balance_to_bytes(&new_balance); let (sigma_proof, zkrp_new_balance) = confidential_proof::serialize_withdrawal_proof(&proof);
confidential_asset::withdraw_to(bob, token, alice_addr, transfer_amount, new_balance, zkrp_new_balance, sigma_proof);
print(&utf8(b"Alice's FA balance after the withdrawal is 50:")); print(&primary_fungible_store::balance(alice_addr, token));
assert!(primary_fungible_store::balance(alice_addr, token) == 50);
print(&utf8(b"Bob's actual balance after the withdrawal is 450")); assert!(confidential_asset::verify_actual_balance(bob_addr, token, &bob_dk, bob_new_amount)); }}旋转加密密钥
Section titled “旋转加密密钥”public entry fun rotate_encryption_key( sender: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>, new_ek: vector<u8>, new_balance: vector<u8>, zkrp_new_balance: vector<u8>, sigma_proof: vector<u8>)public entry fun rotate_encryption_key_and_unfreeze( sender: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>, new_ek: vector<u8>, new_confidential_balance: vector<u8>, zkrp_new_balance: vector<u8>, rotate_proof: vector<u8>)public entry fun rollover_pending_balance_and_freeze(sender: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>)rotate_encryption_key 函数修改用户的 EK,并使用新 EK 重新加密实际余额.
此函数在继续之前检查待处理余额是否为零,确保用户在旋转过程中不会丢失资金.
为了简化旋转过程:
- 必须首先通过调用
rollover_pending_balance_and_freeze滚动并冻结待处理余额. 这可以防止在密钥旋转期间处理新交易. - 然后可以使用
rotate_encryption_key_and_unfreeze旋转 EK 并解冻.
#[test_only]module confidential_asset_addr::rotate_example { /// ...
fun rotate(bob: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>) { let bob_addr = signer::address_of(bob);
// 这是一个仅用于测试的函数,因此我们不需要担心密钥对的安全性。 let (bob_current_dk, bob_current_ek) = twisted_elgamal::generate_twisted_elgamal_keypair(); let (bob_new_dk, bob_new_ek) = twisted_elgamal::generate_twisted_elgamal_keypair();
let bob_current_ek_bytes = twisted_elgamal::pubkey_to_bytes(&bob_current_ek); let bob_new_ek_bytes = twisted_elgamal::pubkey_to_bytes(&bob_new_ek);
let bob_amount = 100;
confidential_asset::register(bob, token, bob_current_ek_bytes); confidential_asset::deposit(bob, token, (bob_amount as u64));
// 我们需要滚动待处理余额并冻结代币以防止任何新存款进入。 confidential_asset::rollover_pending_balance_and_freeze(bob, token);
print(&utf8(b"Bob's encryption key before the rotation:")); print(&confidential_asset::encryption_key(bob_addr, token));
assert!(confidential_asset::verify_actual_balance(bob_addr, token, &bob_current_dk, bob_amount));
let current_balance = confidential_balance::decompress_balance(&confidential_asset::actual_balance(bob_addr, token));
let (proof, new_balance) = confidential_proof::prove_rotation( &bob_current_dk, &bob_new_dk, &bob_current_ek, &bob_new_ek, bob_amount, ¤t_balance );
let ( sigma_proof, zkrp_new_balance ) = confidential_proof::serialize_rotation_proof(&proof);
// 旋转加密密钥后,我们解冻代币以允许新存款。 confidential_asset::rotate_encryption_key_and_unfreeze( bob, token, bob_new_ek_bytes, confidential_balance::balance_to_bytes(&new_balance), zkrp_new_balance, sigma_proof );
print(&utf8(b"Bob's encryption key after the rotation:")); print(&confidential_asset::encryption_key(bob_addr, token));
// 请注意,这里我们使用新的解密密钥来验证实际余额。 assert!(confidential_asset::verify_actual_balance(bob_addr, token, &bob_new_dk, bob_amount)); }}public entry fun normalize( sender: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>, new_balance: vector<u8>, zkrp_new_balance: vector<u8>, sigma_proof: vector<u8>)public fun is_normalized(user: address, token: Object<Metadata>): boolnormalize 函数确保实际余额减少到 16 位块以实现高效解密.
这仅在 rollover_pending_balance 操作之前是必要的,后者要求实际余额事先归一化.
所有其他函数,例如 withdraw 或 confidential_transfer,都隐式处理归一化,因此在这些情况下不需要手动归一化.
#[test_only]module confidential_asset_addr::normalize_example { /// ...
fun normalize(bob: &signer, token: Object<Metadata>) { let bob_addr = signer::address_of(bob);
// 这是一个仅用于测试的函数,因此我们不需要担心密钥对的安全性。 let (bob_dk, bob_ek) = twisted_elgamal::generate_twisted_elgamal_keypair();
let bob_ek_bytes = twisted_elgamal::pubkey_to_bytes(&bob_ek);
let bob_amount = 500;
confidential_asset::register(bob, token, bob_ek_bytes); confidential_asset::deposit(bob, token, (bob_amount as u64));
// 滚动函数是唯一需要事先归一化实际余额的函数, // 并且在执行后无论待处理余额如何都会使其未归一化。 confidential_asset::rollover_pending_balance(bob, token);
assert!(!confidential_asset::is_normalized(bob_addr, token));
confidential_asset::deposit(bob, token, (bob_amount as u64));
// 在执行第二次滚动之前,必须归一化实际余额。 // 如果您尝试滚动未归一化的余额,将会出现错误: // confidential_asset::rollover_pending_balance(bob, token);
let current_balance = confidential_balance::decompress_balance(&confidential_asset::actual_balance(bob_addr, token));
let ( proof, new_balance ) = confidential_proof::prove_normalization( &bob_dk, &bob_ek, bob_amount, ¤t_balance );
let (sigma_proof, zkrp_new_balance) = confidential_proof::serialize_normalization_proof(&proof);
confidential_asset::normalize( bob, token, confidential_balance::balance_to_bytes(&new_balance), zkrp_new_balance, sigma_proof );
assert!(confidential_asset::is_normalized(bob_addr, token)); assert!(confidential_asset::verify_actual_balance(bob_addr, token, &bob_dk, bob_amount));
// 一旦余额归一化,就可以执行滚动。 // 请注意,像 `withdraw` 和 `confidential_transfer` 这样的函数不需要事先归一化实际余额, // 因为 zk-证明保证实际余额在其执行后是归一化的。 confidential_asset::rollover_pending_balance(bob, token); }}